The cutting process involves the costs related to direct material, direct labor, and the overheads related to the cutting department. Consider the equivalent units of the production are 10,000 units and the cost per unit is USD 3 per unit in the cutting department. In job order cost production, the costs can be directly traced to the job, and the job cost sheet contains the total expenses for that job. Process costing is optimal when the costs cannot be traced directly to the job. For example, it would be impossible for David and William to trace the exact amount of eggs in each chocolate chip cookie.
- Eventually, costs have to be allocated to individual units of product.
- Process costing and job order costing are both acceptable methods for tracking costs and production levels.
- In many companies, each stage of the production process is usually handled by a different department.
- Job order costing and process costing are the accounting systems used to record the costs expended to produce a product.
- In an exam, use the first in first out (FIFO) method if the percentage completion of each element of opening WIP is given.
Manufacturing Costs
- While both systems produce a cost of goods sold for a given period, Process Costing focuses on the product’s progression through various stages of production.
- This percentage is a key part of the calculation to assign costs to work-in-process inventory, and so can be used to shift costs into or out of the current period to modify reported levels of profitability.
- Regardless of the costing system used, manufacturing costs consist of direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- So the costs in Process 2 will include everything happening in that process, plus the costs that are attached to the partially completed product transferred in from Process 1.
- It is also impossible to trace the exact amount of hickory in a drumstick.
The cost accounting methodology used for this scenario is process costing. The cost for the direct material, direct labor, and overheads is assigned to the process which is then allocated for the batch of production. The process costing is suitable for the manufacturing companies where identical/homogenous products are produced and there is no gap in the process of production. Process costing and job order costing are both acceptable methods for tracking costs and production levels.
Process costing vs job order costing
Each business will have different processing departments, depending on the product they are making. The difference between process costing and job order costing relates to how the costs are assigned to the products. In either costing system, the ability to obtain and analyze cost data is needed.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
Process Costing is a system of product cost allocation used in merchandising and industry. The main objective is to allocate total manufacturing costs to the various products according to the proportion of resources consumed by each product. This problem is handled through the concept of equivalent units of production. The process costing procedure is explained in more detail in the next example. There are situations whereby companies manufacture a broad mix of products and find it difficult to accurately assign actual costs to each type of product; in such instances, using standard costs can be very useful. After a production run is finished, the total costs that are accumulated based on standard costs are then compared to the actual total costs, and the difference between them is added to a variance account.
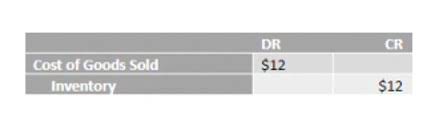
In addition to setting the sales price, managers need to know the cost of their products in order to determine the value of inventory, plan production, determine labor needs, and make long- and short-term plans. They also need to know the costs to determine when a new product should be added or an old product removed from production. You cannot calculate the total output of the period by just taking the sum of completed units and work in process (ending inventory) because units in the work-in-process inventory are not 100% complete. The calculation for the equivalent units of the production is an estimate which is not fully accurate.
The inaccuracy of the work in process may result in the misstatement of the financial reporting. Hence, the percentage of the completion is 80% in respect of the direct material. The completion of the percentage is assigned to create ease in the process of cost allocation for the https://www.bookstime.com/articles/net-realizable-value processed units. Process Costing helps companies make critical decisions based on accurate information. It allows companies to track product cost performance by production location or department—information that can be used to help determine which products are most profitable.
Get the flow of actual units
Yes, many services are produced in a manner similar to manufacturing goods. For example, when an airline provides transportation for passengers the way it would produce any product. Process costing is generally used in industries that deal with chemicals, distilled products, canned products, food products, oil refineries, edible oils, soap, paper, textiles, and others. It’s not much difficult to keep a detailed record of these inputs in the process. Further, the process of the computation is easy to understand and flexible for making the changes. Oil is pumped from the ground, transported, refined, and placed in storage.
2: Comparison of Job Costing with Process Costing

[Note that the two methods give different valuations for the closing WIP.]In the weighted average method, no distinction is made between units of opening inventory and new units introduced to the process during the accounting period. A process cost system process costing (process costing) accumulates costs incurred to produce a product according to the processes or departments it goes through on its way to completion. Companies making paint, gasoline, steel, rubber, plastic, and similar products use process costing.
Basic Managerial Accounting Terms Used in Job Order Costing and Process Costing

