
However, if the number is too high, it could mean the company is not leveraging its assets as well as it otherwise could be. These are short-term debts owed by a company for goods or services received. For example, in 2018, Apple Inc. reported accounts payable of $55.9 billion, mainly to suppliers like Foxconn for manufacturing components. Typically, vendors provide terms of 15, 30, or 45 days for a customer to pay, meaning the buyer receives the supplies but can pay for them at a later date. These invoices are recorded in accounts payable and act as a short-term loan from a vendor. By allowing a company time to pay off an invoice, the company can generate revenue from the sale of the supplies and manage its cash needs more effectively.
Liabilities
- A retailer has a sales tax liability on their books when they collect sales tax from a customer until they remit those funds to the county, city, or state.
- The role of a project accountant depends on the project being worked on.
- Companies may plan for these expenses if they anticipate an outcome requiring them to do so.
- A formal loan agreement that has payment terms that extend beyond a year are considered notes payable.
- If one of the conditions is not satisfied, a company does not report a contingent liability on the balance sheet.
- Current liabilities could also be based on a company’s operating cycle, which is the time it takes to buy inventory and convert it to cash from sales.
Long-term liabilities have higher interest rates due to the wide gap between the time of borrowing and repayment. Liabilities also have implications for a company’s cash flow statement, as they may directly influence cash inflows and outflows. For example, a mortgage payable types of liability accounts impacts both the financing and investing sections of the cash flow statement. As the company makes payments on the mortgage, the principal portion of the payment reduces the mortgage payable, while the interest portion is accounted for as an interest expense.
Different Types of Liabilities in Accounting

Different types of liabilities are listed under each category, in order from shortest to longest term. Accounts payable would be a line item under current liabilities while a mortgage payable would be listed under long-term liabilities. While liabilities & expenses are used in similar contexts, they are distinct accounting terms, & each plays a distinct role.
Types of Liabilities
A liability is anything that’s borrowed from, owed to, or obligated to someone else. It can be real like a bill that must be paid or potential such as a possible lawsuit. A company might take out debt to expand and grow its business or an individual may take out a mortgage to purchase a home.
Examples of Liability Accounts
Your accounts payable balance, taxes, mortgages, and business loans are all examples of things you owe, or liabilities. They’re recorded in the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet. Current liabilities are obligations that a company needs to settle within a year, whereas long-term liabilities extend beyond a year. Current liabilities are typically more immediate concerns for a company, as they are short-term financial obligations that require quick action.
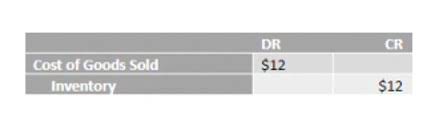
Contingent liabilities are potential liabilities that depend on the outcome of future events. For example contingent liabilities can become current or long-term if realized. Liabilities are an operational standard in financial accounting, as most businesses operate with some level of debt. Unlike assets, which you own, and expenses, which generate revenue, liabilities are anything your business owes that has not yet been paid in cash. A liability is a financial obligation a company owes to other parties. These stem from past transactions or events and result in an outflow of resources, usually in the form of money, products, or services.

Tax Accounting
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling

